

Manifest files are reused across snapshots to avoid rewriting metadata that is slow-changing. The data in a snapshot is the union of all files in its manifests. A snapshot represents the state of a table at some time and is used to access the complete set of data files in the table.ĭata files in snapshots are tracked by one or more manifest files that contain a row for each data file in the table, the file’s partition data, and its metrics. The table metadata file tracks the table schema, partitioning config, custom properties, and snapshots of the table contents. All changes to table state create a new metadata file and replace the old metadata with an atomic swap. Table state is maintained in metadata files. This allows writers to create data files in-place and only adds files to the table in an explicit commit. This table format tracks individual data files in a table instead of directories. Both read-optimized and write-optimized formats will be available. Formats – Underlying data file formats will support identical schema evolution rules and types.Tables will support evolving partition schemes. Reads will be planned using predicates on data values, not partition values. Storage separation – Partitioning will be table configuration.Dependable types – Tables will provide well-defined and dependable support for a core set of types.Schema evolution supports safe column add, drop, reorder and rename, including in nested structures.
#Time zone overlap calculator full
#Time zone overlap calculator how to
Appendix E documents how to default version 2 fields when reading version 1 metadata. Version 1 of the Iceberg spec defines how to manage large analytic tables using immutable file formats: Parquet, Avro, and ORC.Īll version 1 data and metadata files are valid after upgrading a table to version 2. Tables may continue to be written with an older version of the spec to ensure compatibility by not using features that are not yet implemented by processing engines. The format version number is incremented when new features are added that will break forward-compatibility-that is, when older readers would not read newer table features correctly.
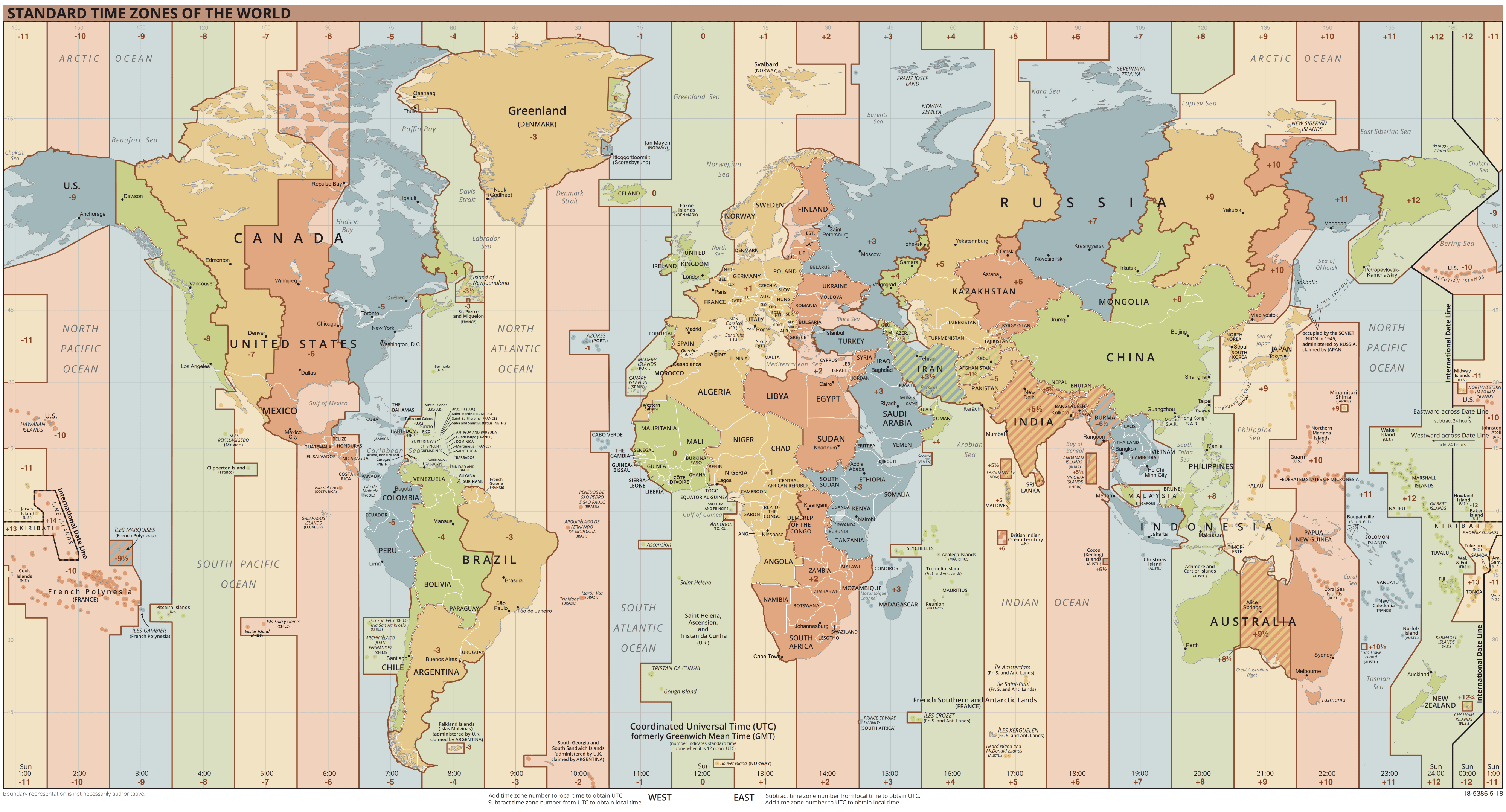
Versions 1 and 2 of the Iceberg spec are complete and adopted by the community. This is a specification for the Iceberg table format that is designed to manage a large, slow-changing collection of files in a distributed file system or key-value store as a table.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
